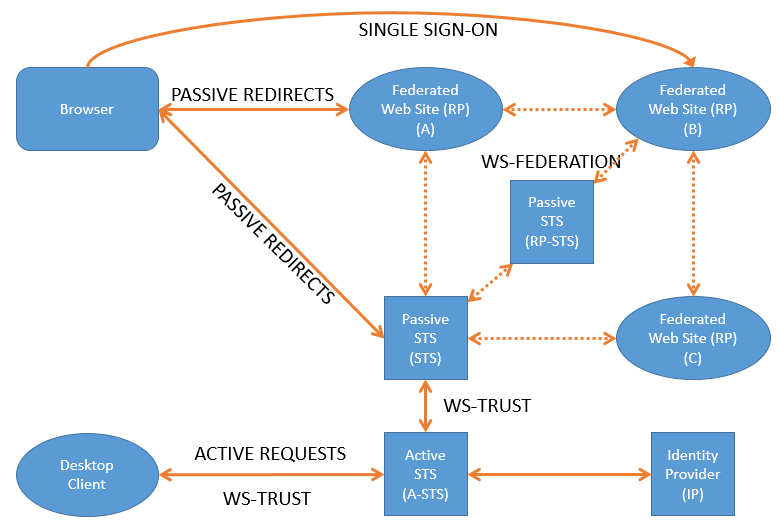
Figured that I would start a post dealing specifically with all the terms we find in the Identity world. Ill add to this post as time goes on…
I am providing the image above to try and assist to Identity the different components. The terms used in the image above is for WS-Federation.
Common terms
- SAML, depending on its use it can refer to a token format or a protocol for exchanging identity information.
- Token is a secured message of varying format that contains the identity of the authenticating party.
- Identity, is a unique description of the authenticating party.
- Claims, a claim is a documented statement about an identity usually used for the process of security identification. It can refer to any attribute about an Identity like Name, Surname, Email, Roles etc.
- SSO, Single sign-on allows a client to access resources on multiple interconnected independent systems that trust the same STS.
WS-Trust terms
- WS-Trust is a specification for sharing of identity tokens – In its most basic definition it allows for the building of trust between 2 parties. The trust is established through the use of certificates. The certificates with which the token is signed acts as proof of identity.
- STS, is a Security Token Service that creates a specific type of token containing the Identity of the authenticating party. an STS can be a IP-STS, RP-STS or A-STS.
- A-STS or Active STS is a STS servicing “active” client applications that are state aware and capable to know if a user is authenticated or not and have the internal knowledge on how to authenticate.
WS-Federation terms
- WS-Federation builds on WS-Trust by allowing several independent web-sites to join together in their trust of a common STS.
- Passive STS is a IP-STS or RP-STS servicing browser based applications. The passive term refers to the way that the client is redirected between the federated website and the passive sts. Often the client using the browser is unaware that he is being redirected between 2 independent systems.
- RP, Relying Party relies on a outside party like a IP-STS to provide an identity.
- IP, is a Identity Provider. an Identity provider provides the identity of the authenticating party. This will be some sort of directory like a Active Directory but could easily be a custom database with user information.
- IP-STS, This is the combination of the IP & STS into a single component.
- RP-STS, Relying Party Security Token Service provides authentication, based on tokens from other STS’s as credentials.
- STS Chaining, refers the connection / trust between a RP-STS and IP-STS.
SAML terms
- SP, This is the SAML version of the WS-Federation RP. SP stands for Service provider and refers to the application the end user is trying to use.
- IDP, This is the SAML version of the WS-Federation IP-STS. IP stands for Identity provider and refers to the application that will be doing the authentication of the user.
- SP-Initiated, This is a SAML authentication mode. With this mode the user uses his browser to access the SP and the SP then redirect the un-authenticate user to the IP.
- IP-Initiated, This is a SAML authentication mode. In this mode the user signs directly into the IP and then the IP provides the user with a list of applications to which the user can then be directed to.
Many of the STS terms above get explained very well by Vittorio Bertocci over here.